Posts
- Metaprogramming Ruby
- Metaprogramming Ruby: Ascent
- Create a cron job to run our script everyday.
- Script contains fetching app info from iTunes connect and update the same on our servers.
-
To start, I created a basic cron job which posts notification on mac osx every 20 minutes. Notification reminds user to take a break from work.
-
Also, a created a cron job to remind me continuously about informing team about standup status. Till I act on the notification, notification is continuously posted every 15 minutes in the morning for few hours. Once action is taken, notification is posted next day. BTW this makes sure it only reminds on weekdays.
- Comic version A Stick Figure Guide to the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
- FIPS Document link
- Purdue University
- Youtube video
Ruby meta-programming
#Ruby meta-programming
Before starting with ruby meta-programming, one should clearly understand the ruby object model. Here are some great videos explaining the same:
RubyMonk provides two courses on meta-programming.
Please go through the same if you are a beginner to meta-programming.
ALL THE BEST!!!
Ruby Koans
RubyKoans is an excellant approach to learn the Ruby language, syntax, structure, and some common functions and libraries. This also teaches you a testing culture. This requires tests to be fixed in order to progress.
My solutions are available here.
##Development Tweaks
Real time updates
To check the solution, one has to run rake command everytime to know progress status. Smells like there is a need for automation.
I used kicker which is a lean, agnostic, flexible file-change watcher using OS X FSEvents.
You may add this simple .kick file to the koans project.
process do |files|
execute("rake")
end
To start,
$ kick
Now whenever you modify any test and save the file, kicker will show you the current status.
Git
To share solutions with everyone, I used git and pushed solutions to Github repo.
Prefill commit message
This project saves all the current progress in .path_progress file.
Sample file:
0,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5,6,6,6,6,6,6,6,6,6,7,7,7,7,7,7,7,7,7,7,8,8,8,8,8,8,8,8,8,8,9,9,9,9,10,10,10,10,10,10,11,11,11,12,12,12,13,13,13,13,13,13,14,14
Whenever a koan is finished, koan number is automatically appended to .path_progress.
Now trick is to prefill git commit message with the current progress. I created this prepare-commit-msg hook to solve this problem.
#!/bin/sh
commitMessage=$(./`git rev-parse --git-dir`/get-progress)
echo "Finish koan $commitMessage\n $(cat $1)" > $1
This hook uses another script get-progress which prints the current progress(i.e. koan number).
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
PROGRESS_FILE_NAME = '.path_progress'
contents = []
if File.exists?(PROGRESS_FILE_NAME)
File.open(PROGRESS_FILE_NAME,'r') do |f|
contents = f.read.to_s.gsub(/\s/,'').split(',')
end
end
print contents.last
Duplicates in .path_progress
Everytime rake is run, current progress (i.e. koan number) is added to .path_progress which leads to unnecessary file changes. This creates further problems when .path_progress is added to git repo.
Time to fix neo.rb. Add following code to add_progress method.
def add_progress(prog)
@_contents = progress
# return if already added to progress
return if prog.to_i == progress.last.to_i
Bash Gmail Scripts
Here’s my efforts on writing wrapper script to send mails from terminal. Looking forward to use this in other useful scripts.
Automation
This sunday’s challenge was to maintain a service which provides the latest version info of an iOS application.
Previously, we used to update this info manually each time new version gets approved and released on appstore. But as one can easily guess, this leads to problems like delays, misses updating the same.
“Mistakes tend to occur whenever work is manual”
Here comes the savior…Fastlane’s Spaceship. Using this one can fetch iOS app info from iTunes connect and developer portal.
Now lets automate:
By the way, this led me to explore cron jobs more and think about solving my day to day problems with cron jobs.
By the end of day, I again fell in love with cron jobs.
AES
AES-128-ECB and AES-128-CBC
Here 128 refers to number of bits.
128 bits = 16 bytes
Block
AES has to be applied on blocks of input data. Each block is of 16 bytes length.
2D Matrix Representation
16 bytes block can be represented in a 4 x 4 matrix. Example: “YELLOW SUBMARINE” can be represented as:
'Y' 'O' 'U' 'R'
'E' 'W' 'B' 'I'
'L' 'M' 'N'
'L' 'S' 'A' 'E'
Note: Bytes has to be filled columnwise and not rowwise. Aim is to spread out the message. This is one of the ideas of crypto DIFFUSION.
Operations
Encryption Decryption
---------- ----------
addRoundKey addRoundKey
subBytes invSubBytes
shiftRows invShiftRows
mixColumns invMixColumns
Details about these operations can be found in my friend’s blog here.
Block Cipher Encryption + Decryption
message = decrypt(encrypt(message))
As it is clear from the expression, decryption is the reverse of encryption. Once you understand encryption, just reverse the steps you have done in encryption and you will get decryption.
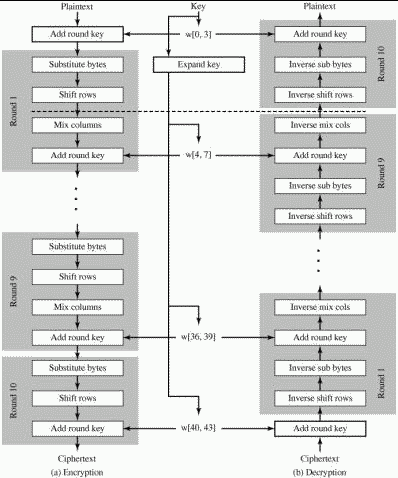
Key expansion
Block cipher encryption/decryption consists of multiple rounds of operations. Each time you apply addRoundKey() operation, it needs a different key to be added.
Given an initial key, say k of length 16 bytes, we can apply a procedure to get expanded keys. As we will see later, in block cipher operation addRoundKey() is applied 11 times. We will use key expansion procedure to get 10 new keys.
key k
key k1 = expandKey(k)
key k2 = expandKey(k1)
.
.
.
key k10 = expandKey(k9)
These keys k, k1, …, k10 has to be found in advance before starting with block cipher encryption and decryption process.
Block cipher encryption
begin =
addRoundKey
middle = 9 rounds
subBytes
shiftRows
mixColumns
addRoundKey
end =
subBytes
shiftRows
addRoundKey
Block cipher decryption
begin =
addRoundKey
middle =
invShiftRows
invSubBytes
addRoundKey
invMixColumns
end =
invShiftRows
invSubBytes
addRoundKey
Note: Following figure shows that block cipher decryption is just the reverse of block cipher encryption process.
AES-128-ECB
Encryption
For each of the blocks, feed plaintext block and key to block cipher encryption and thats it. We will get ciphertext corresponding to each block of plaintext. Combine them and you are done!!!

Decryption
For each of the blocks, feed ciphertext block and key to block cipher decryption and thats it. We will get plaintext corresponding to each block of ciphertext. Combine them and you are done!!!
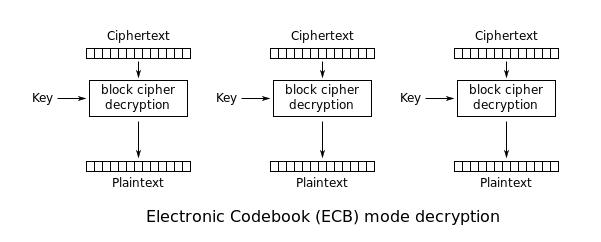
Note: In ECB mode, operations on each block of plaintext is independent of other blocks. This means two different blocks of similar plaintext will give same ciphertext. This fact related to duplicates can be misused to crack AES-ECB.
AES-128-CBC
CBC overcomes the problem in ECB mode. While performing block cipher encryption/decryption on a block, it depends upon the ciphertext of the previous block operation.
For the first block, we take initialization vector(IV). For rest of the blocks IV is the same as ciphertext of previous blocks.
Encryption
Before applying block cipher encryption process, perform plaintext xor IV.
Decryption
After applying block cipher decryption process, perform output xor IV to get plaintext.

PKCS#7 Padding
The message to be encrypted can be of any length. To make sure that the length is a multiple of block size(16 bytes here), we will add PKCS#7 padding. Example, “YELLOW SUBMAR” will be changed to “YELLOW SUBMAR\u0003\u0003\u0003”. More details here.
Tools
Use openssl command line tool to encrypt/decrypt as per ECB and CBC modes.
Refer to post to understand usage.
Further reading
subscribe via RSS